However, both the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq 100 made new highs by August 2020. With us, you’ll trade with leverage – this means you’ll only need a small deposit, known as margin, to gain full exposure. So then what can we do to really cushion our losses, and even make some money in a bear market? A bear market is commonly defined as a stock market decline of 20% or more as reflected in a broad index like the Standard & Poor’s 500 or the Nasdaq Composite. That doesn’t make it any easier to anticipate them, predict how long one will last, or estimate the depth of the decline.

Focus on those growth stocks that stand to lose a lot of market share and ride them down, but keep a firm hand on the brakes if the market begins to recover. The bear market phenomenon is thought to get its name from the way in which a bear attacks its prey—swiping its paws downward. This is why markets with falling stock prices are called bear markets. Just like the bear market, the bull market may be named after the way in which the bull attacks by thrusting its horns up into the air. One definition of a bear market says markets are in bear territory when stocks, on average, fall at least 20% off their high.
Start learning
Trying to recoup losses can be an uphill battle unless investors are short sellers or use other strategies to make gains in falling markets. A market correction is a price movement that goes against an established bull or bear market, which in the case of bear markets is a short-term rise of prices. A bear market is a period during which prices fall significantly following recent highs – this is normally indicated by a minimum price drop of 20%.

Meanwhile, the gains made at high risk during a bear market don’t count double. It’s all well and good to be greedy when others are fearful if you’re Warren Buffett. (In fact, the Oracle of Omaha said that is the only time to be greedy.) Either way, you’re not Warren Buffett, and your retirement savings don’t need a hero during periods of high risk. Note however that all investment and trading contains risk, and past performance does not guarantee future returns.
Generative AI can save marketing pros 5 hours per week, according to research
Event-driven bear markets are caused by a specific event, such as a natural disaster or a financial crisis. The signs of a weak or slowing economy are typically low employment, low disposable income, weak productivity, and a drop in business profits. In addition, any intervention by the government in the economy can also trigger a bear market. When asset prices start to fall and the downtrend shows signs of continuation, traders can borrow the instrument and sell it at the current (higher) price.
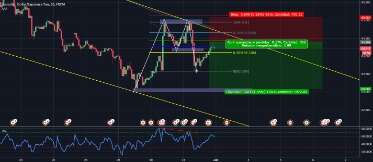
- The strict definition of a bear market is when the stock market, often judged by a national stock index, has closed for the day 20% down or lower from its 52-week high.
- IG International Limited is licensed to conduct investment business and digital asset business by the Bermuda Monetary Authority.
- This kind of bear market can last for months or years as investors shun speculation in favor of boring, sure bets.
- With negative investor sentiments on the rise, prices are likely to tumble even further, making it risky to trade in a bear market.
- If you’re not sure whether you belong to the small minority, you probably don’t.
The U.S. major market indexes were again close to bear market territory on December 24, 2018, falling just shy of a 20% drawdown. Between 1900 and 2018, the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) had approximately 33 bear markets, averaging one every three years. One of the most notable bear markets in recent history coincided with the global financial crisis occurring between October 2007 and March 2009. During that time the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) declined 54%. The global COVID-19 pandemic caused the most recent 2020 bear market for the S&P 500 and DJIA.
How to trade in a bear market
However, with the right strategies, it is possible to trade options in a bear market and still turn a profit. In this article, we will discuss some of the key strategies for trading options in a bear market and how to maximize your profits. Short-selling enables traders to speculate on a falling share price, and if the prediction is correct, make a profit. It’s important to note that even in bear markets, the price action could go either way. Please ensure you understand how this product works and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing money.
It is an extremely risky trade and can cause heavy losses if it does not work out. A short seller must borrow the shares from a broker before a short sell order is placed. The short seller’s profit and loss amount is the difference between the price where the shares were sold and the price where they were bought back, referred to as “covered.”
Learn to trade
Stocks were driven down by the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, which brought with it mass lockdowns and the fear of depressed consumer demand. During this period, the Dow Jones fell sharply from all-time highs close to 30,000 to lows below 19,000 in a matter of weeks. Stock prices generally reflect future expectations of cash flows and profits from companies.
COMPANY & PARTNERS
It typically describes a condition in which securities prices fall 20% or more from recent highs amid widespread pessimism and negative investor sentiment. This could be an opportunity to lock in profits regularly, but it’s important to remember that prices can move up every now and then, even in bear markets. A covered call option is a strategy where you own the underlying stock and sell call options on it. This strategy can be profitable in a bear market because if the stock price goes down, the call options will expire worthless and you can keep the premium as income. Additionally, if the stock price doesn’t go down as much as you expect, you can still make a profit on the difference between the stock price and the strike price of the call option. By a happy coincidence, lower-risk stocks have generated long-term returns similar to those of riskier ones, despite the lower risk.